
David Andrews Online Portfolio
Job Assignment
The Assignment Method (Also known as the Hungarian Method)
The assignment method is a way of discerning optimal machine/job combinations.
Using the Assignment Method:
We start with a list of four jobs, 1,2,3,4, and four machines, a,b,c,d. How do we assign each job to a machine?
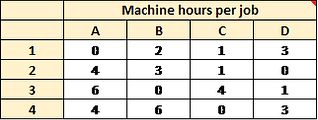
1. Create a table listing the time it would take for each machine to complete each job.

-
Next, isolate the best job/machine combinations. This is done by subtracting the smallest number in every row from every number in that row (including itself).
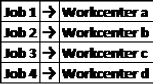
-
The objective is to cover the all zeros with horizontal or vertical lines, and have the quantity of lines be greater than or equal to the number of rows or columns. Since we need 4 lines to cover all zeros, this example is complete. The Location of the zeros is what assigns the jobs. So, the location of the zeros in the above table gives us job assignments.
What happens if we do not have enough lines on the first trial? More explanation available in this link: Click Here.
Job Sequencing
Why use job scheduling?
The focus of job scheduling is to increase process efficiency and reduce downtime. Proficient job scheduling leads to a more efficient and economical manufacturing process.
Job Scheduling Methods: Johnsons rule.
Johnsons rule is a simple way to optimally schedule jobs between two machines.
Using Johnsons Rule, Schedule the below jobs.

-
Set up a row with the same # of columns as there is jobs.

2. Select the job with the shortest process time. If the shortest process time is in column 1, schedule that job first. If the shortest process time is in column 2, schedule that job 2nd. (if more than one job competes for lowest run time, arbitrarily choose one.)

3. Eliminate the selected job from the list.
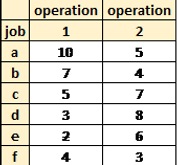
4. Repeat steps 2&3 Until all jobs are filled.
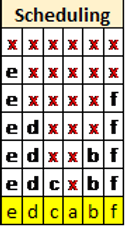
Johnsons Rule: Gantt Chart Formation
-
Make a two row Gantt Chart, one row for each operation. Place the operation with the higher sum of hours in the first row.

2. Schedule the operation the first row (operation 2) in the order determined by step 4 above.

3. Assign the jobs for the second operation. There will be an unavoidable downtime from the difference in work time of the two operations. Allocate downtime wherever best fit.

This is the Final schedule, with minimal possible downtime.